New Open Access AI-Mind Publication on Region Based Pooling
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have opened up new opportunities for the fields of cognitive neuroscience and clinical brain health research. AI-Mind aims to harness AI-based tools for estimating the risk of dementia in individuals affected by mild cognitive impairment (MCI). The project not only collects a comprehensive set of data, including biomarkers, sociodemographic information, digital cognitive test scores, and electroencephalography (EEG) data but employs a combination of traditional machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL)-based algorithms.
When using the DL method with new EEG data, a challenge is that the architecture cannot handle changes in the number of EEG channels. This means the number of channels can not change during training or when using the model. These strict hardware limits make it hard to use DL models in clinical settings and to scale them up.
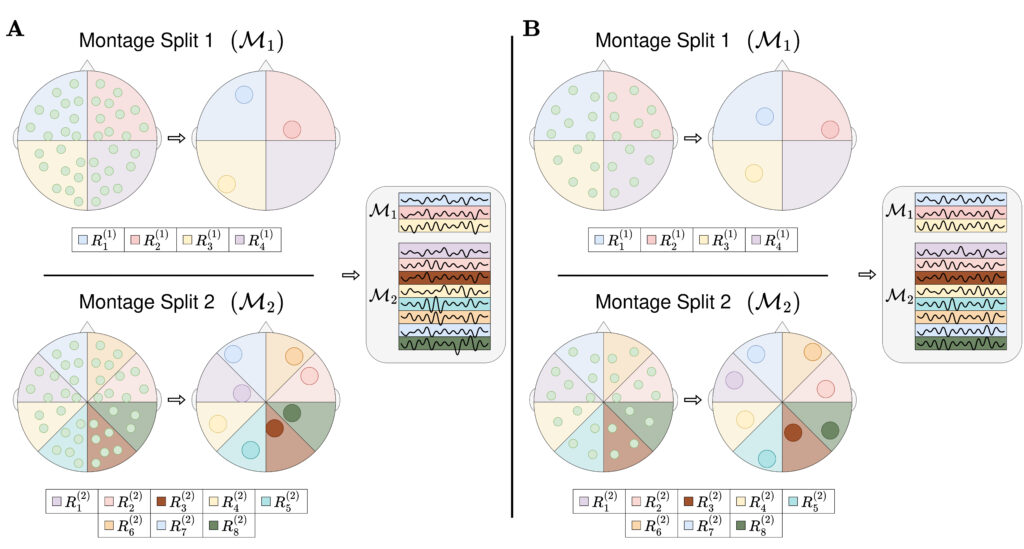
In a recent publication “Introducing Region Based Pooling for handling a varied number of EEG channels for deep learning models“, authors shed light on the innovative methodologies being employed within the AI-Mind project. The paper presents the so-called Region Based Pooling (RBP) technique for handling the varied numbers of EEG channels. This approach involves splitting EEG montages into distinct regions and merging channels within the same region to create a region representation. By combining traditional ML with DL-based algorithms, the AI-Mind project aims to extract nuanced patterns from complex and unstructured data, thus enhancing the accuracy of dementia risk estimation.
Speaking on the significance of their involvement in the AI-Mind project, PhD student from Oslo University Hospital who presents the research results in the mentioned paper highlights: “Being part of AI-Mind provides a unique opportunity to work with an extensive amount of data derived from the AI-Mind study. This collaborative effort allows us to delve into unexplored territories, pushing the boundaries of cognitive health research.” – Thomas Tveitstøl says.
The paper also delves into a comprehensive discussion on data handling, outlining the study’s limitations and offering insights into future directions for research. With its interdisciplinary approach and cutting-edge methodologies, AI-Mind is poised to make significant strides in the quest to address the dementia challenge.

The figure from the publication represents the region based pooling. The EEG montage is split into multiple regions. All channels in the same region are pooled into a region representation. Go to the publication to read teh full description.
This insightful paper published in Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, aligning with the European Commission’s Open Science policy, is available in full open access under the link: https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2023.1272791